
Do you happen to be a Doctor Who or a Star Trek fan? Have you ever wondered how force field, time travel, teleportation or invisibility could become a reality without breaking the laws of physics? If yes, then this book by Michio Kaku is a must for you!
Physics of the impossible discusses technologies of tomorrow by introducing topics of fundamental physics to the reader, such as relativity, uncertainty principle and how LASER works, etc. This book will help one grasp how physics is applied to the advancement of human civilization.
The guiding philosophy of the book is: If, in principle, something is possible, then it can be achieved. Like going to the moon was possible but only an engineering problem. In similar way, futuristic tech may only be an engineering solution away.
One can divide technology into three different classes of impossibilities, meaning how unlikely they are going to be, given our current understanding of physics.
- Class I impossibilities are "technologies that are impossible today, but that do not violate the known laws of physics."
- Class II impossibilities are “technologies that sit at the very edge of our understanding of the physical world."
- Class III impossibilities are “technologies that violate the known laws of physics but their development would mean a crucial shift in our understanding of physics!"
The author of the book is renowned American theoretical physicist Michio Kaku who is known for his contributions to the string field theory. Physics of the impossible is primarily aimed for aspiring physicists, that is, undergraduate and graduate students; but engineers will also enjoy it maximum.
Why did Kaku decide to write a whole 350-pages book predicting the technology of tomorrow? Because, he's am ardent science fiction fan and strongly believes that what is impossible today, might be commonplace tomorrow.
For example: William Thomson Kelvin, a mathematical physicist and creator of the Kelvin scale had declared that “heavier than air” flying machines would be impossible.
Ernest Rutherford, the physicist who discovered nucleus of an atom and won the Nobel Prize always thought the idea of atom bomb was impossible and compared it to moonshine (a crazy thought).
Such technologies were considered impossible because the basic laws of physics and science were not understood as well at the time as they'd subsequently be.
Michio Kaku has shown in the book, with numerous examples, how scientists and technicians around the world are trying to realize technology of tomorrow...today...in their own individual laboratories.
There is also something for history fans in the book. Historical development of telepathy and artificial intelligence has been described in a manner that makes you want to keep on reading on. It gives you a sense of fulfilment to have learned what all has been done.
And as you unravel the secret of alien technologies (which you might only have seen on TV shows and movies so far) you will be inspired to join forces with scientists and engineers to harness the true power of nature.
The book Physics of the impossible will surely renew your confidence in the endless possibilities of physics. The phrase, "one of a kind" is well suited for such a book because not only it entertains you but also teaches a multitude of things about how science works.







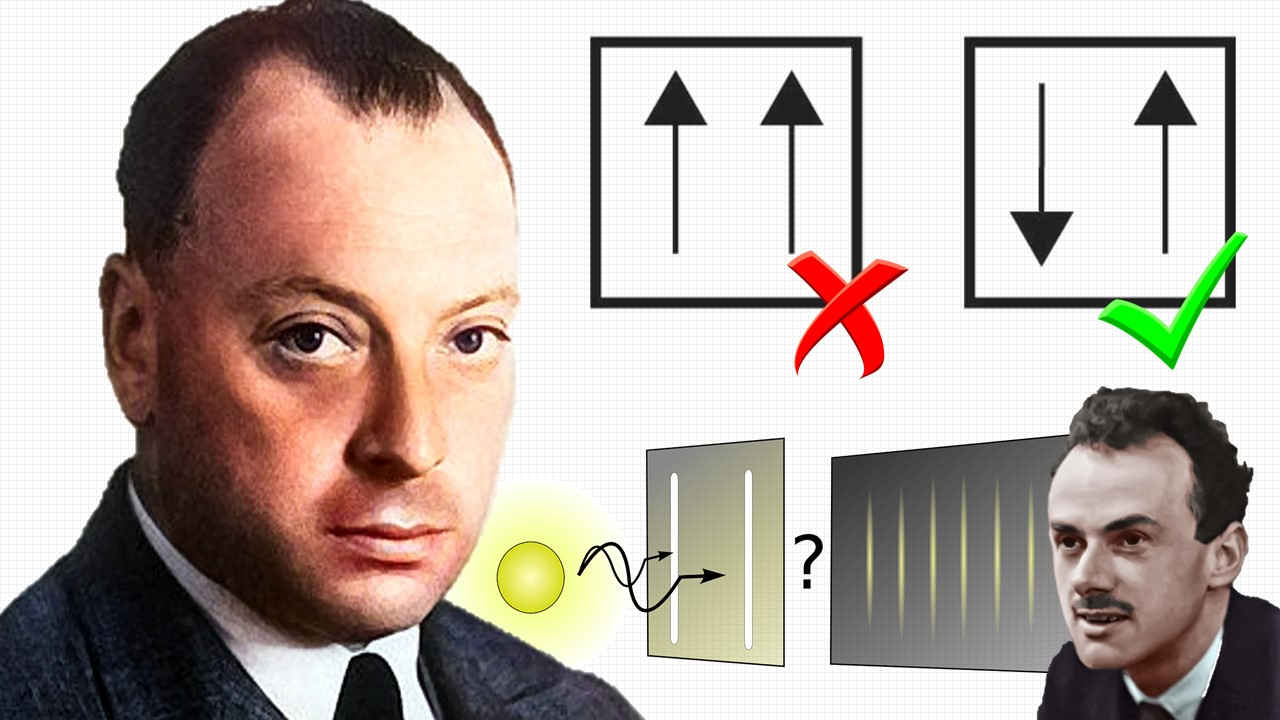



















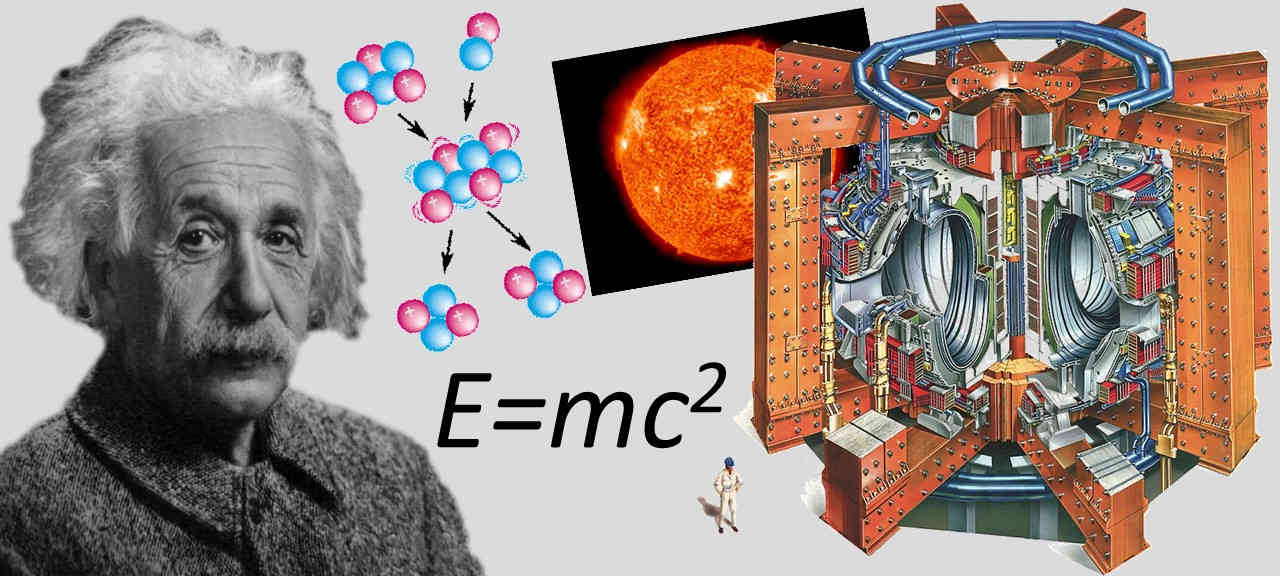

 Physics, astronomy and science history blog for students
Physics, astronomy and science history blog for students