
4 Unsolved Mysteries About The Higgs Boson

7 Funny Quotes By Physicist Wolfgang Pauli
Prophet Dirac
 |
| Dirac, Pauli |
Elusive Neutrino
Trolling Heisenberg
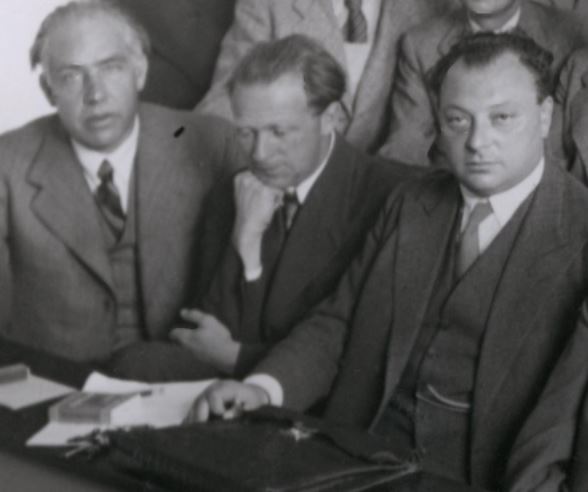 |
| Bohr, Heisenberg, Pauli |
Parity violation
Bad science
Why so serious?

On knowledge
Why You Should Read The Order of Time

 |
| Source: Penguin |
5 Life Lessons You Can Learn From Marie Curie



10 Engineers Who Won Nobel Prize In Physics
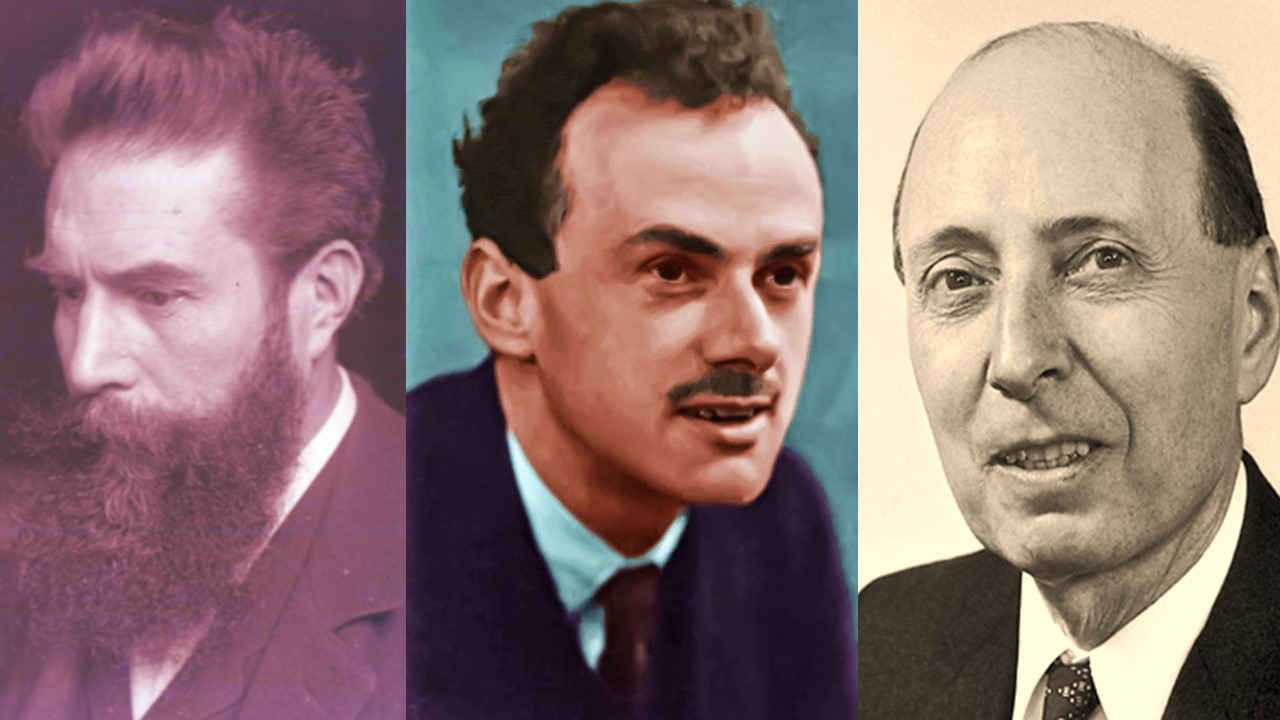

John Bardeen
Henri Becquerel

Wilhelm Röntgen
Eugene Wigner
Paul Dirac
Dennis Gabor
Jack Kilby
Simon van der Meer

Shuji Nakamura
Ivar Giaever
10 Famous Physicists Who Played Chess
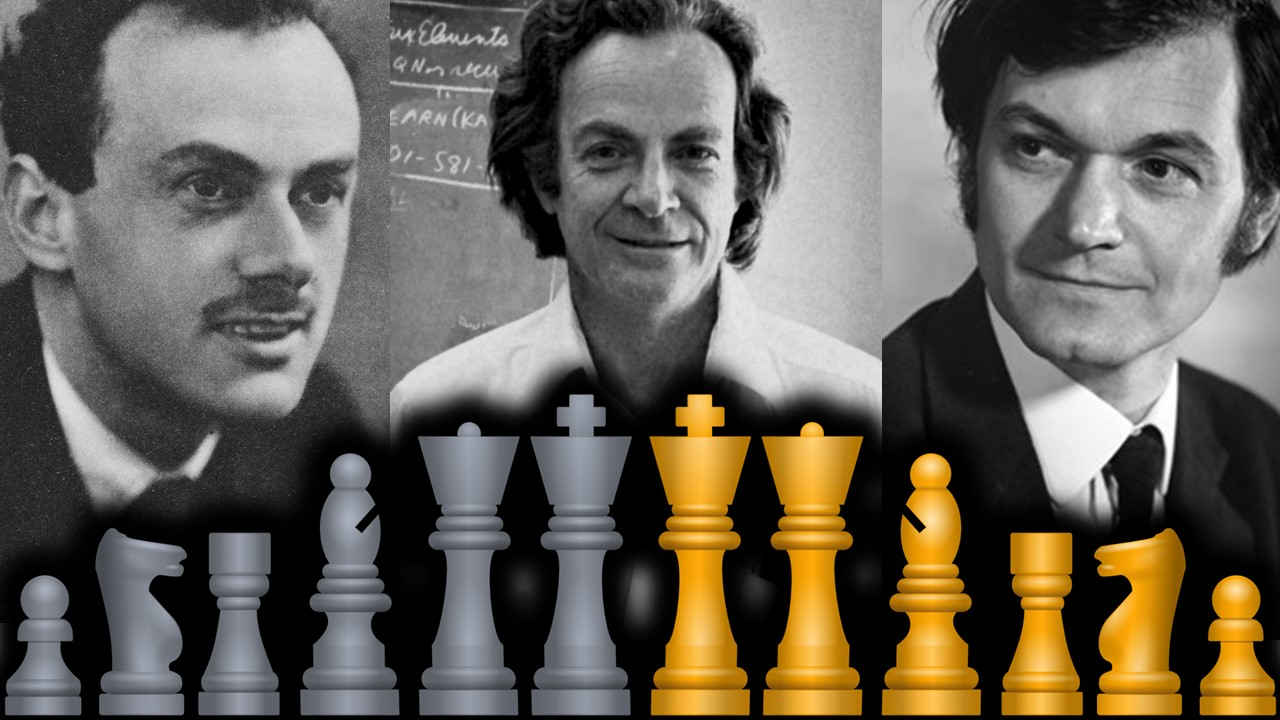

Paul Dirac

Roger Penrose
Stephen Hawking
 |
| picture credit: pinterest |
Albert Einstein
Richard Feynman
Werner Heisenberg
Edward Teller
 |
| picture: ESVA |
William Henry Bragg
Erwin Schrödinger
Max Planck
Engineer Who Won The Nobel Prize Twice In Physics

 |
| Replica of the first transistor |
If you make a list of people – politicians, scientists, sportspersons, etc – who have had the greatest impact on the 20th century, John's name would certainly make it to the top ten. Because, without his work, none of the modern technologies would be possible.
10 Albert Einstein Quotes To Succeed In Life

Apart from making groundbreaking discoveries in physics, Albert Einstein also played the role of a motivational guru quite often. So, following are 10 Einstein quotes that will change your life.
1. Everyone sits in the prison of his own ideas; he must burst it open, and that in his youth, and try to test his ideas on reality. [Meaning: Don't keep delaying what you really want to do. Try it out for who knows what is possible?]
2. Joy in looking and comprehending is nature's most beautiful gift. Never lose a holy curiosity for it has its own reason for existing. [Meaning: Every child is born curious. Keep your mind open to new adventures.]
3. Try to become not a man of success, but try rather to become a man of value. Because, only a life lived for others is a life worthwhile. [Meaning: Our relationships are just as important as goals.]
4. Life is like riding a bicycle. In order to keep your balance you must keep moving. [Meaning: Enjoy the ride. Don't be afraid to fall.]
5. Don't think about why you question, simply don't stop questioning. Don't worry about what you can't answer, and don't try to explain what you can't know. [Meaning: Curiosity is a quality one must never let go of. Ask questions as they will lead you to life's answers.]
6. Blind obedience to authority is the greatest enemy of truth. [Meaning: Don't follow people blindly.]
7. The value of a college education is not the learning of many facts but the training of the mind to think. [Meaning: Learn how to think, not what to think.]
8. I never think of the future. It comes soon enough. [Meaning: Live in the moment. Act now.]
9. The mediocre mind is incapable of understanding the man who refuses to bow blindly to conventional prejudices and chooses instead to express his opinions courageously and honestly. [Meaning: Break the mould you were born into.]
10. If A is success in life, then A = x + y + z. Work is x, play is y and z is keeping your mouth shut. [Meaning: Work hard. Play hard. Stay humble.]
Who Was Lise Meitner?

Collaboration with nephew
Her role in World War I
Early education & PhD
Professorship & war
Help by Bohr
Manhattan Project
Dinner with President
Chemical elements
Nobel Prize snub
Critical of friends
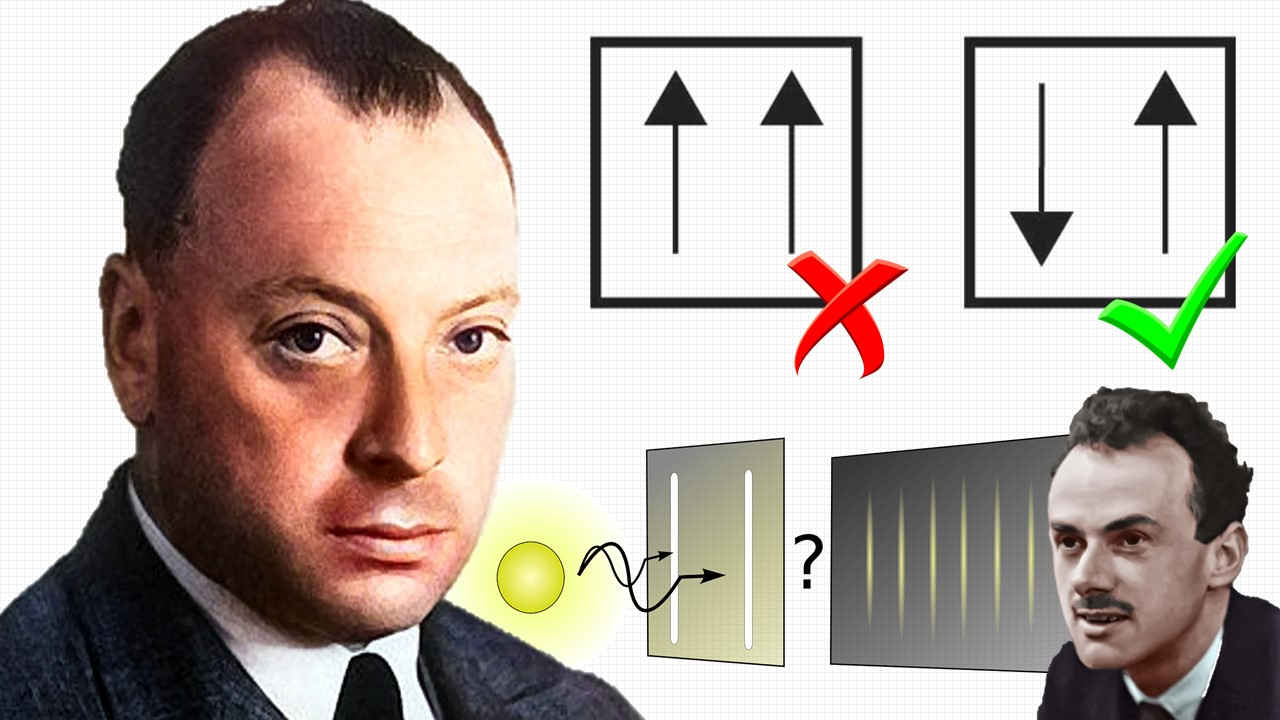
This Is How Dirac Predicted Antimatter

But some may consider Dirac an even greater scientist due to many reasons. While Newton, in his day, became much involved with pseudosciences such as alchemy; he even attempted to reconcile science with faith through his writings. Paul Dirac, on the other hand, an outspoken agnostic, remained true to scientific path, and went on to make many significant contributions to the theory of everything.
Furthermore, while Newton was considered arrogant, too full of himself, who often made use of his authority to dismiss others' opinions. Dirac, on the other hand, was a lean, meek, shy young fellow, who suffered agonies if forced into any kind of small talk. He coined the term Fermion after Italian physicist Enrico Fermi, despite him having worked on the equation which governed the behavior of Fermions.
So that was a little background information on the man that was Paul Dirac. Unfortunately, he never was popularized enough, in fact, hardly anyone knows anything about who he was or what he did in his scientific career. Even so, his work is of primary importance to electronics, especially how electrons flow in the transistor, devices which form the building blocks of any modern-day computer.
What's more: his biggest discovery, prediction of anti-particle, has inspired numerous science fiction writers to create a mirror world in their stories, the collision of which with the real world, would lead to a whole lot of catastrophic activity in the lives of their characters. This is based upon Dirac's work that when matter and antimatter collide, they annihilate one another.
In the early twentieth century, Dirac, who had just completed his engineering degree, was unemployed. But this made him choose math as a career and thank goodness he did so! Because, a great quantum revolution was ongoing and Dirac, who had merely remained an observer, was keen on becoming a part of it.
Everybody at that time was talking about a young Austrian physicist named Erwin Schrödinger. He just had formulated wave mechanics, that is, an equation which explained the behavior of electron inside an atom. The wave equation, so it was called, gave the probability of finding the electron at any given point inside the atom.
Dirac realized that Schrödinger's wave equation was inconsistent with special theory of relativity. In other words, even though the equation was enough to describe the electronic motion at low velocity, it was yet unable to do the same at speeds approaching that of light. Dirac took this challenge upon himself to find a solution for it.
Unlike other physicists, those who insisted that revelations in physics be firmly grounded on experimental data, (and rightly so) Dirac relied heavily on mathematical consistency instead. To him, if the equation he found had mathematical beauty, then he just assumed that he was going on the correct path. This just goes on to show that Paul Dirac was more of a mathematician rather than a staunch physicist.
After many years, in 1928, Dirac modified the Schrödinger's equation to make it agreeable with Einstein's special relativity. His groundbreaking equation also defined the concepts of spin and magnetic moment of electron. While developing his equation, Dirac realized that Einstein's famous energy-mass relation, E=mc², was only partially right. The correct formula, he claimed, should be E=±mc², the minus sign because one has to take the square root of E²=m²c^4, which was a subtle correction indeed.
But then, according to an axiom of physics, matter particles always tend to the state of lowest energy - for stability. Therefore, the negative sign in E=mc² would imply that all the electrons tumble down to infinitely large negative energy. That is, an electron in a positive energy state (bound or free) should be able to emit a photon and make a transition to a negative energy state. This process could continue forever giving off an infinite amount of light!
Clearly, that isn't the case in the actual, stable universe; real electrons do not behave in such a way. So it made Dirac think of a solution to the problem: he proposed a theoretical model called the Dirac Sea in which he imagined that all the negative energy states were already occupied, meaning, that an electron in positive state could not tumble down to negative energy (since according to Pauli's exclusion principle, no two electrons could share a single energy state).
If a particle of this negative energy sea is given sufficient energy it is possible for it to rise into a positive energy state. A resulting "hole" would be created in the negative energy sea. This hole should have the same mass as the original electron but behave like a positively-charged particle.
Dirac wrote in 1931, after being suggested by Oppenheimer, that this hole was an anti-electron; a re-combination with electron should annihilate both of them. Because, when the electron comes into contact with the hole it spontaneously fills the hole and consequently must release the excess energy that went in.
In 1932, while examining the composition of cosmic rays, high-energy particles that move through space at nearly the speed of light, American physicist Carl Anderson discovered the positron. He observed that a particular particle in the ray behaved out of the ordinary. The trajectory suggested that it had to be positively charged but at the same time 1/1,836 the mass of a proton, exactly that of an electron.
In his 1933 Nobel Prize lecture, Dirac suggested that particle-antiparticle should be a fundamental symmetry of nature. He interpreted the Dirac equation to mean that for every particle there existed a corresponding antiparticle, exactly matching the particle mass but with opposite charge. In 1955, antiproton was discovered by University of California, Berkeley physicists.
The success of Dirac equation shows that a mathematical result can manifest itself in the real world. Paul Dirac had once said, "If you are receptive and humble, mathematics will lead you by the hand." That is pretty much true; his work has been described fully on par with the works of Newton, Maxwell, and Einstein before him. Dirac was undoubtedly a genius.









 Physics, astronomy and science history blog for students
Physics, astronomy and science history blog for students