
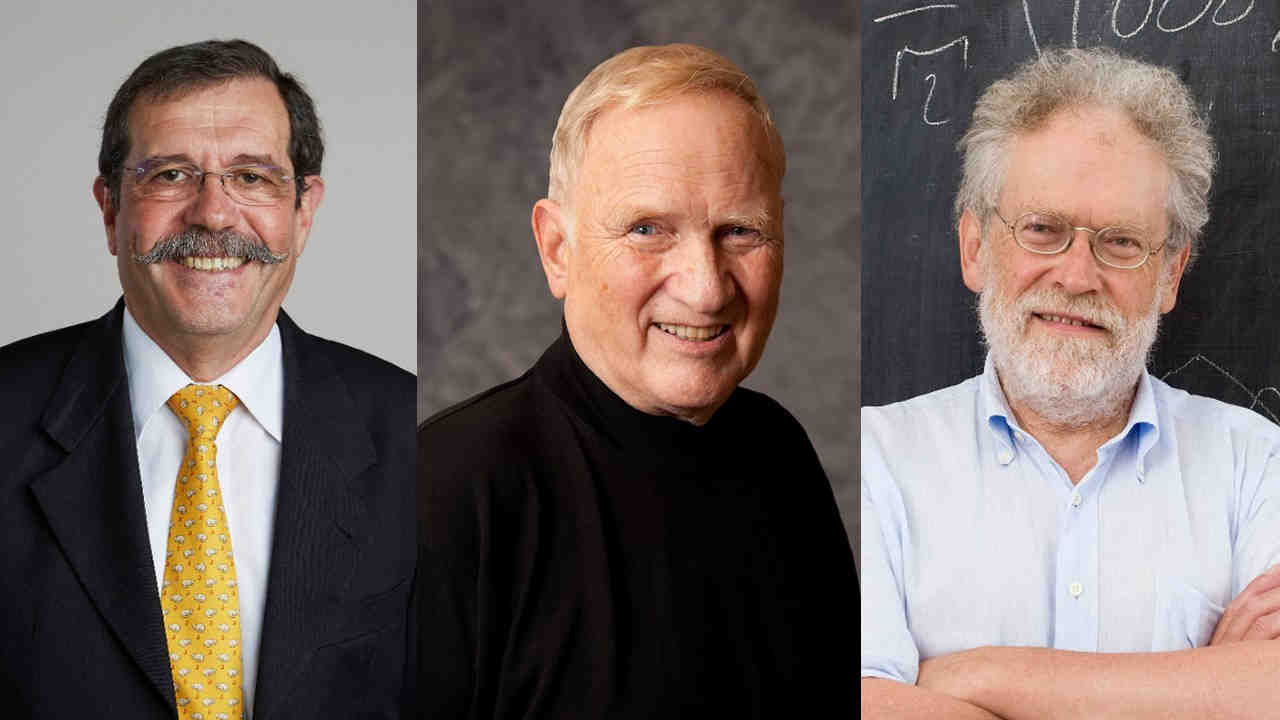
The 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics has been announced to 3 scientists from different nations, whose work has pushed quantum mechanics from a highly conceptual realm to physical devices you can actually hold. The winners are Michel Devoret (France), John Clarke (UK) and John M. Martins (USA).
Their experiments in the 1980s have bridged theory and engineering, paving the way for tomorrow’s quantum technologies, which we actually use today! In simpler terms, they showed decades ago that quantum effects, like tunnelling and discrete energy levels, can manifest in circuits large enough to be held.
What Nobel Committee Said
The Nobel Committee explained why this year's win is crucial for physics and tech world... "they have provided opportunities for developing the next generation of quantum technology, including quantum cryptography, quantum computers, and quantum sensors."
Olle Eriksson, Chair of the Nobel Committee for Physics, said:
It is wonderful to be able to celebrate the way that century-old quantum mechanics continually offers new surprises. Quantum mechanics is the foundation of all digital technology.
 |
| Nobel For Macroscopic Quantum Object |
Nobel Committee noted that the winners' findings have "brought quantum mechanics from the subatomic world onto a chip."
Reaction of Nobel Laureates
The winners' comments suggest that this was unexpected and a meaningful recognition which they will cherish. John Clarke commented: "It never occurred to me that this might be the basis for Nobel prize." He almost collapsed out of surprise!
John M Martins opened his computer, and saw his picture alongside the other winners, and he was "in shock." Michel Devoret was instrumental in making long-term contributions in superconducting quantum circuits, and thankful for the recognition.
The royal society (UK) of which John Clarke is a fellow, said:
Their experiments revealed that the strange laws of quantum physics apply not only at the atomic scale, but in systems big enough to see and touch.
What the winners discovered
The key phenomena involved in the victory are quantum tunnelling and energy quantisation. Quantum tunneling is the phenomenon where a subatomic particle passes through a potential energy barrier that it shouldn't have enough energy to overcome, according to classical physics.
Quantum systems, like electron, can only absorb or emit energy in discrete packets (quanta). In many quantum systems, allowed energy levels are separated by well defined gaps; energy transitions happen when quantum systems, like electron, jump between energy levels.
The breakthrough of the laureates was to show that these effects, long thought to be limited to atoms, molecules or small particles, can appear in macroscopic — i.e. large — systems when engineered correctly.
To study the two phenomena, they carefully controlled parameters like current, voltage, and temperature, and measured the electrical behavior of the circuit which they built using superconducting materials. And all of this was done in the mid 1980s! Their pioneering work led to the technologies in the devices we use today, and will use tomorrow.
How Nobel winners are selected
The Nobel Prizes were established through the will of Alfred Nobel, a scientist, engineer and industrialist, who died in 1896 and left instructions that the bulk of his enormous fortune be used to found annual prizes in Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace.
 |
| Alfred Nobel and Nobel Prize |
Nobel Prize in physics is awarded every year, usually announced in early October. For each year’s Nobel Prize, the nomination process begins in the previous year.
Nomination forms are sent out anonymously to select individuals in the field, around 3000 reputed scientists, in September. They nominate candidates for the coveted prize before Jan 31 deadline, but they cannot nominate themselves.
The Nobel committee reduces the nominee list to a shortlist (often ~15 names) and eventually proposes up to three laureates for the prize. In the earlier days, the prize was also given to a single person as well.
Summing up
The 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics is a reminder that quantum mechanics is not just a set of bizarre formulas for electrons, but a living framework that can manifest in engineered devices. Clarke, Devoret, and Martinis converted quantum phenomena into electrical circuits, closing the gap between theory and practicality.
In awarding this prize, the Nobel Committee highlights that years of careful research in basic physics can lead to major technological change. It shows that big breakthroughs often start as simple questions explored with patience in the physics lab.


















 Physics, astronomy and science history blog for students
Physics, astronomy and science history blog for students